Roll to Roll Coater: Enhancing Continuous Manufacturing Processes
● Introduction
A roll to roll coating machine is an essential technology in the continuous manufacturing process of flexible substrates. This technique involves coating a flexible material, such as plastic film, metal foil, or paper, as it moves through various stages of processing. R2R coating is widely used in industries such as electronics, solar cells, packaging, and biomedical devices due to its efficiency, scalability, and cost-effectiveness.
● Importance of Roll to Roll Coating
1. **High Throughput**: R2R coating allows for continuous processing, significantly increasing production rates compared to batch processes.
2. **Cost Efficiency**: The continuous nature of R2R coating reduces downtime and material waste, leading to lower production costs.
3. **Scalability**: R2R processes can be easily scaled up to meet high-volume manufacturing demands.
4. **Versatility**: Suitable for a wide range of applications and materials, making it a versatile choice for various industries.
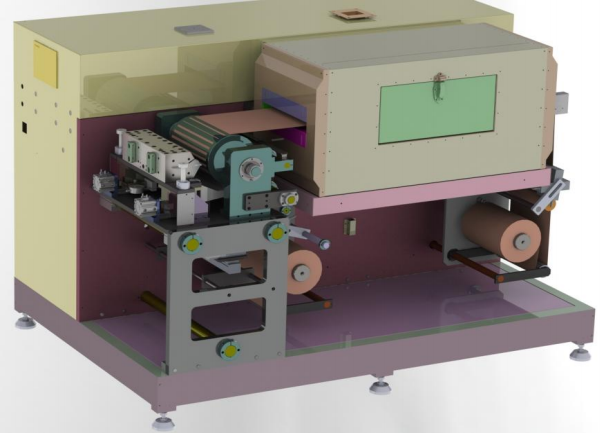
● Key Components of a Roll to Roll Coater
1. **Unwinder**:
- The unwinder holds and feeds the roll of substrate into the coating system. It ensures consistent tension and alignment of the substrate as it unwinds.
2. **Coating Station**:
- The core component where the coating material is applied to the substrate. Different techniques can be used depending on the application and material properties.
3. **Drying/Curing System**:
- After the coating is applied, it needs to be dried or cured. This can involve thermal ovens, UV lamps, or other curing technologies to solidify the coating.
4. **Rewinder**:
- The rewinder collects the coated substrate, winding it into a roll for further processing or packaging. It also maintains proper tension and alignment.
5. **Control System**:
- Ensures precise control over the coating process, including substrate tension, coating thickness, drying/curing parameters, and speed. Often includes computerized systems for monitoring and adjustments.
● Coating Techniques
1. **Slot Die Coating**:
- Involves applying a precise amount of coating material through a narrow slot onto the substrate. Ideal for uniform coatings with tight thickness control.
2. **Gravure Coating**:
- Uses a gravure roll with engraved cells to pick up and transfer the coating material to the substrate. Suitable for high-speed applications and intricate patterns.
3. **Doctor Blade Coating**:
- A blade applies a coating material onto the substrate, controlling the thickness by adjusting the blade gap. Used for various coating thicknesses and materials.
4. **Spray Coating**:
- Involves spraying the coating material onto the substrate using nozzles. Suitable for irregular surfaces and achieving fine coatings.
5. **Dip Coating**:
- The substrate is dipped into a coating solution and then drawn out, allowing the coating to adhere. Commonly used for uniform, thin coatings.
● Applications
1. **Flexible Electronics**:
- R2R coating is crucial in manufacturing flexible electronic components, such as printed circuit boards, displays, and RFID tags. It allows for the deposition of conductive, dielectric, and protective layers.
2. **Solar Cells**:
- Used in the production of flexible photovoltaic cells, where thin layers of semiconductor materials are coated onto flexible substrates.
3. **Packaging**:
- R2R coating is employed in producing barrier films, labels, and decorative coatings for packaging materials.
4. **Biomedical Devices**:
- Used in coating flexible medical sensors, wearable devices, and drug delivery systems.
5. **Textiles**:
- R2R coating processes are used to apply functional coatings to textiles, such as waterproofing, anti-bacterial treatments, and conductive coatings for smart fabrics.
● Advantages and Challenges
#Advantages
1. **Efficiency**: Continuous operation reduces downtime and increases throughput.
2. **Uniformity**: Provides consistent and uniform coatings, essential for high-quality products.
3. **Flexibility**: Can handle a variety of substrates and coating materials, making it adaptable to different applications.
# Challenges
1. **Complexity**: The process can be complex, requiring precise control over various parameters to ensure quality.
2. **Initial Costs**: High initial investment in equipment and setup.
3. **Material Compatibility**: Not all materials are suitable for R2R coating, requiring careful selection and testing.
● Future Trends
1. **Advanced Materials**: Development of new coating materials with enhanced properties, such as improved conductivity, flexibility, and environmental resistance.
2. **Nanotechnology**: Incorporation of nanomaterials into R2R processes to produce high-performance coatings for electronics and energy applications.
3. **Automation and AI**: Integration of advanced automation and artificial intelligence for real-time process control and optimization.
● Conclusion
The Roll to Roll coater is a pivotal technology in the field of continuous manufacturing, enabling the efficient and cost-effective production of high-quality coated materials. Its versatility and scalability make it indispensable across various industries, from electronics and solar cells to packaging and biomedical devices. As technology advances, R2R coating processes will continue to evolve, driving innovation and expanding the potential applications of this essential manufacturing technique.




 Online service
Online service +86 13174506016
+86 13174506016
